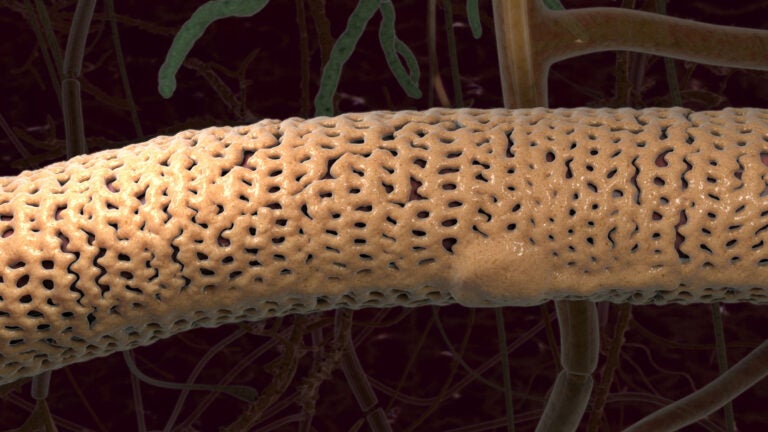
Damage to pericytes, the layer of cells that wrap around blood vessels in the brain, leads to decline in cognition and is accelerated in people who carry the APOE4 gene. (Image/Courtesy of Jim Stanis and Arthur W. Toga, USC Stevens Neuroimaging and Informatics Institute)
Alzheimer’s gene triggers early breakdowns in blood-brain barrier, predicting cognitive decline
Although scientists have long known APOE4 is a leading risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease, they were unsure how exactly it drives a decline in memory. USC researchers now believe they have an answer.
New USC research reveals how APOE4 — a genetic culprit for Alzheimer’s disease — triggers leaks in the brain’s plumbing system, allowing toxic substances to seep into the brain areas responsible for memory encoding and other cognitive functions.
The damage is linked to future problems in learning and memory, even when the disease’s signature sticky plaques have not appeared. The findings suggest that the smallest blood vessels in the brain, which form the blood-brain barrier, might be a potential target for early treatment.
The study appears today in Nature.
“This study sheds light on a new way of looking at this disease and possibly on treatment in people with the APOE4 gene, looking at blood vessels and improving their function to potentially slow down or arrest cognitive decline,” said senior author Berislav Zlokovic, director of the Zilkha Neurogenetic Institute at the Keck School of Medicine of USC. “Severe damage to vascular cells called pericytes was linked to more severe cognitive problems in APOE4 carriers. APOE4 seems to speed up the breakdown of the blood-brain barrier by activating an inflammatory pathway in blood vessels, which is associated with pericyte injury.”
How the APOE4 gene leads to a damaged blood-brain barrier
Scientists have long known that the APOE4 gene — which occurs in up to 14% of the population — increases the probability of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Until now, it’s been unclear how different pathologies determine the course of the disease in its early stages, or what underlying mechanisms lead to cognitive decline in APOE4 carriers.
Zlokovic’s previous research shows that people who develop early memory problems also experience the most leakage in their brain’s blood vessels — independent of amyloid plaque or tau, two common contributors to Alzheimer’s. The leakage starts when cells called pericytes, which line the walls of blood vessels in the brain and maintain blood-brain barrier integrity, are damaged. These injured pericytes can be detected with a unique biomarker, developed by Zlokovic’s lab in 2015, which shows up in cerebrospinal fluid.
For this study, scientists used standard memory tests to check the participants’ cognitive abilities and their neuropsychological performance. They also used advanced neuroimaging and employed the biomarker that indicates damage to the brain’s blood vessels.
In participants who had the APOE4 gene, researchers found damaged capillaries in the brain’s memory center, the hippocampus and medial temporal lobe. The damage correlated with increased levels of a protein that causes inflammation, cyclophilin A — an early sign of the disease in people already at higher risk of developing Alzheimer’s.
Zlokovic, who became director of the Zilkha Neurogenetic Institute in 2012, pioneered the concept that a breakdown in the blood-brain barrier contributes to cognitive impairment and dementia. The Zilkha Neurogenetic Institute opened at Keck School of Medicine in 2003 with a $20 million donation from Los Angeles businessman Selim Zilkha, who later contributed $10 million more to the effort.
In addition to Zlokovic, other authors are Axel Montagne, Daniel A. Nation, Abhay P. Sagare, Giuseppe Barisano, Melanie D. Sweeney, Ararat Chakhoyan, Maricarmen Pachicano, Elizabeth Joe, Amy R. Nelson, Lina M. D’Orazio, John Ringman, Helena C. Chui, Yining Chen, Judy Pa, Meng Law, Peter S. Conti, Arthur W. Toga and Lon Schneider, all of the Keck School of Medicine; David P. Buennagel and Michael G. Harrington of Huntington Medical Research Institutes; Tammie L. S. Benzinger and Anne M. Fagan, John C. Morris of Washington University School of Medicine; Eric M. Reiman of the Banner Alzheimer’s Institute; Richard J. Caselli of the Mayo Clinic; and Julia TCW of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
The study was supported by a combination of grants from the National Institutes of Health, the Alzheimer’s Association, Cure Alzheimer’s Fund, the Foundation Leducq Transatlantic Network of Excellence for the study of Perivascular Spaces in Small Vessel Disease and Open Philanthropy.
Additional support is from L.K. Whittier Foundation and National Institute on Aging, the state of Arizona, and from Avid Radiopharmaceuticals Inc., owned by Eli Lilly and Co.



